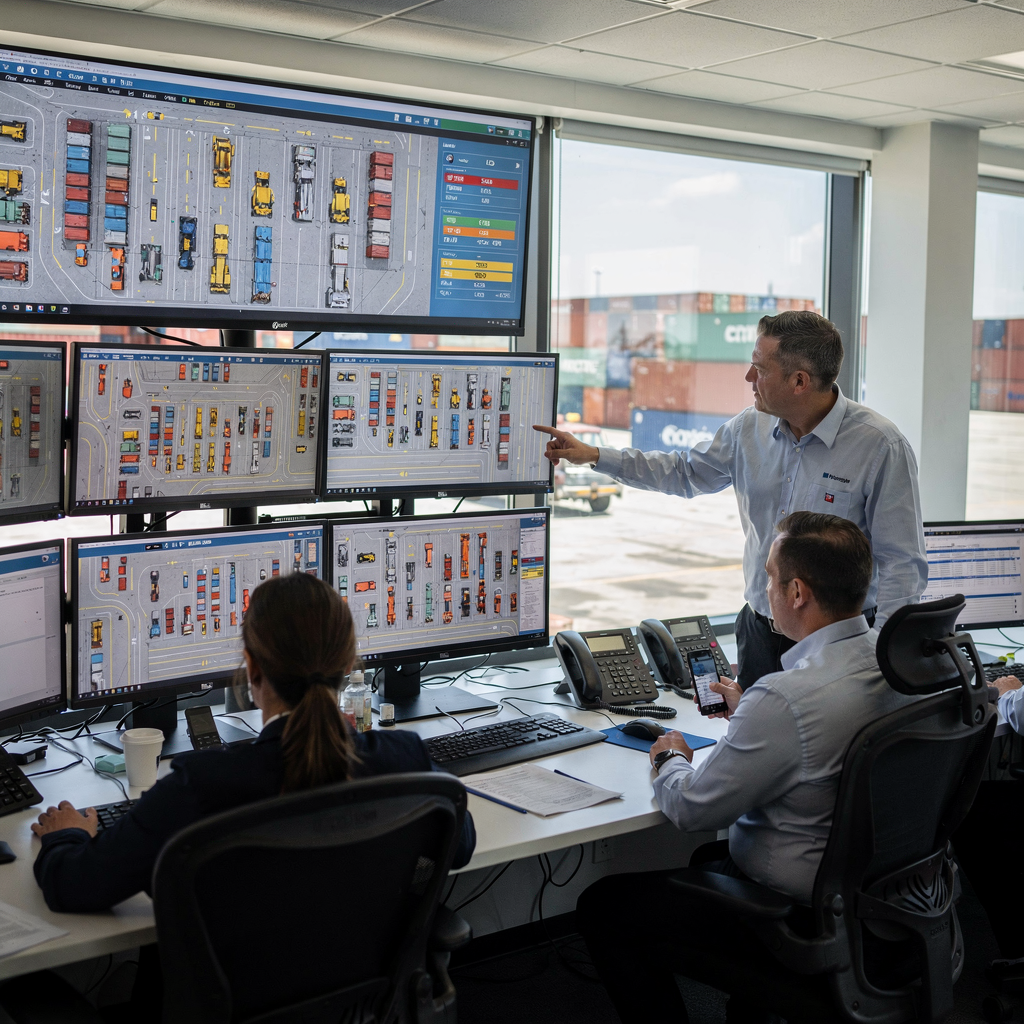
migration approach
Define clear objectives and scope before you start any migration. First, state the business outcomes you expect, and link them to measurable KPIs such as vessel turnaround time and throughput. A clear migration plan helps the migration team focus on priorities and reduces uncertainty for operations. For example, ports that adopt advanced Terminal Operating Systems report up to a 30% increase in operational efficiency and a 20% reduction in vessel turnaround time, which helps justify the work and clarify trade-offs for stakeholders (study) and supports a successful migration.
Engage stakeholders across operations, IT, marine, gate divisions, and commercial teams. Invite planners, stevedores, gate controllers, and the tos vendor to joint workshops so that everyone aligns on scope. Also include security and legal owners. This reduces dependency on single experts and preserves tribal knowledge. A clear governance framework should assign roles, set decision points, and create communication channels. Use an RACI or similar model to state who approves key changes, who tests, and who signs off on production cut-over.
Set up a migration steering committee that meets weekly, and create an escalation path for operational incidents. Include the expertise of a migration architect to design a detailed migration plan and to identify potential integration issues early. Use lightweight change logs so the whole team tracks every change in requirements, every migration phase, and every risk mitigation step. Link technical tasks to business operations to keep the focus on continuity and resilience. Loadmaster.ai can support this planning by running a sandbox digital twin, which helps validate operational changes and allows the migration team to test new policies before live runs; see our digital twin testing for yard strategy digital twin container yard strategy testing.
Finally, define success criteria and acceptance tests. Include both technical metrics and operational KPIs. Use short feedback cycles to iterate, and record lessons learned from the migration so the organisation improves on each phase. A clear migration approach helps minimize risk, supports business continuity, and prepares teams to complete the migration with minimal disruption and clear expectations throughout the migration.
migration strategies
Adopt parallel running alongside the legacy TOS to validate new workflows, and to keep production systems active while you test. Parallel running gives staff time to train, teams time to troubleshoot integrations, and managers time to measure impacts on throughput. One port operations manager said, “Running the new system alongside the old one was crucial. It gave us confidence and time to resolve issues without impacting daily operations” Source. Use that insight to design safe pilot windows and to limit the amount of downtime during cut-over.
Implement a phased roll-out by module. Start with less risky modules such as reporting or analytics, then progress to yard planning, gate control, and quay operations. A phased implementation reduces risk and provides quick wins so stakeholders stay engaged. Consider three data migration strategies for different data types: big-bang for non-critical historical data, incremental approach for active records, and dual-write for live synchronisation. Use pilot terminals or specific shifts to test integrations before full cut-over. Pilots expose compatibility gaps, reveal performance bottleneck risks, and validate synchronization patterns between modules.
Manage the migration of large data sets by using replication, CDC, and message queues so live updates keep both systems consistent. Design clear rollback paths and contingency plans. Test each rollback in a sandbox environment and document execution steps. Also pay close attention to human factors. Train planners and dispatchers in realistic scenarios so they can handle incidents and reduce human errors. For deeper strategy testing, combine reinforcement-learning agents in a simulation to stress-test new workflows; see our AI-driven yard strategy details for approaches that balance crane productivity and yard quality AI-driven yard strategy.
Finally, use governance and audit trails during phased rollouts to ensure compliance and traceability. The IAPH guidance highlights cybersecurity risks during system transitions and recommends access controls and continuous monitoring to protect gate controls and cargo handling devices (IAPH). These migration strategies form a practical roadmap for teams that need to migrate at speed while avoiding major disruption.

Drowning in a full terminal with replans, exceptions and last-minute changes?
Discover what AI-driven planning can do for your terminal
data migration process
Inventory and classify data for migration. Start with container, vessel, and equipment records, and tag each dataset by criticality, update frequency, and retention rules. Define data for migration and include metadata so teams know schema ownership. Mapping source and target data fields reduces surprises. Use automated scripts to extract and transform records and to preserve data quality. Also perform manual spot audits to catch edge cases and subtle mismatches. This layered validation keeps data integrity high and reduces the risk of data loss when you migrate.
Map the application’s data access patterns to schedule transfers during low-activity windows. Use synthetic loads in a sandbox to measure how long bulk data transfers take and to reveal performance bottleneck areas. Transferring data must respect referential constraints and unique identifiers; otherwise dispatch and billing logic can fail. Build validation checks that compare record counts, checksum values, and business logic outputs. A successful data migration depends on both automated verification and human review cycles. Test rollback routines and verify that backups restore correctly before you move production traffic.
For critical records, use dual-write or change-data-capture so both systems remain in sync. Synchronization must be observed, and you should log conflicts and reconcile them daily. Data updates and changes during cut-over can create race conditions; define rules to resolve writes from different masters. Consider a temporary read-only mode for historical data in the legacy system while active records sync in real time. This approach reduces the chance of inconsistent views for drivers, crane operators, and gate staff.
Successful data migration also needs a data governance plan. Include data stewards, and set thresholds for acceptable error rates. Keep a clear migration checklist and record every step to support audits and to make post-migration troubleshooting easier. Finally, ensure a smooth transition by aligning cut-over windows with vessel schedules and terminal peaks so business operations remain reliable. For additional modelling and testing, simulation models for automated terminal operations can help predict impacts before you migrate simulation models for automated terminal operations.
database migration
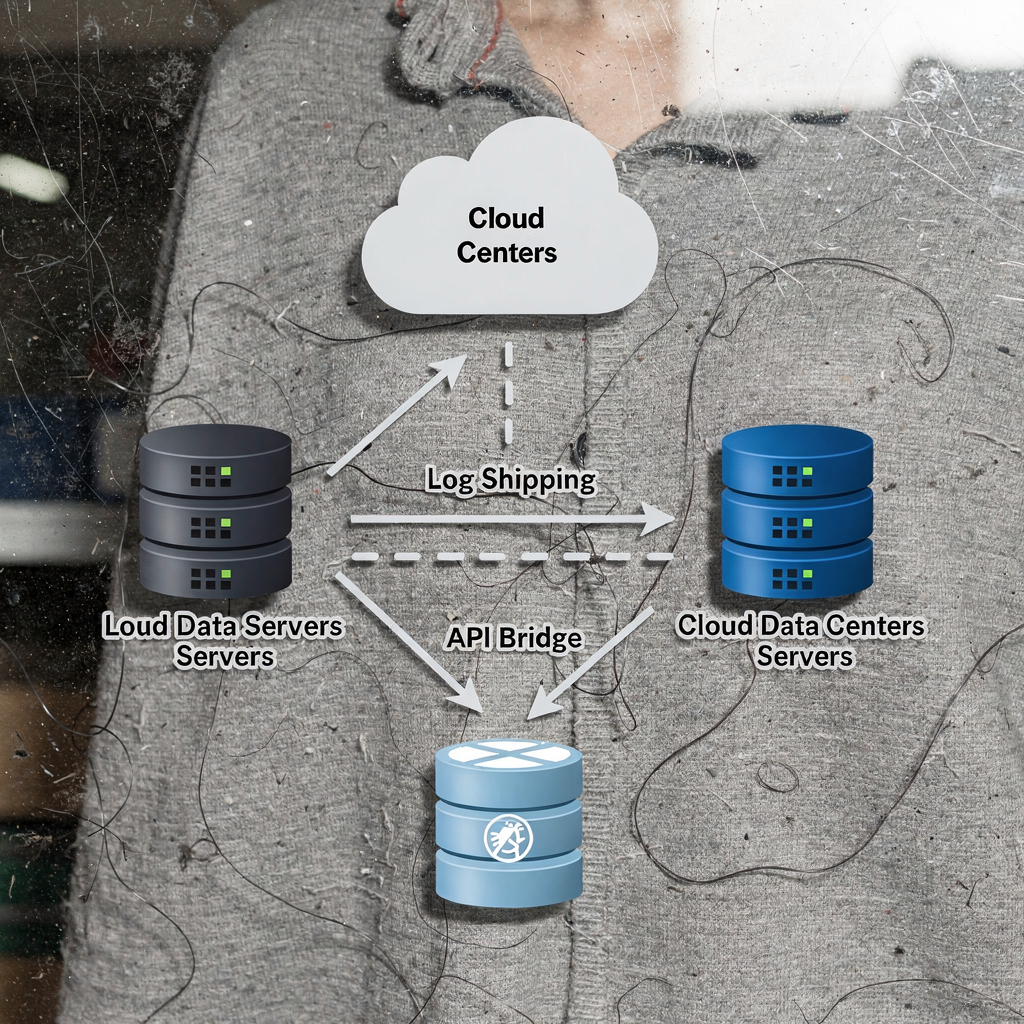
Plan database migration with minimal change windows by using replication, log shipping, and staged switchover. For many terminals, the database systems are the backbone that supports equipment dispatch, gate control, and billing. Migrate core databases while keeping a hot replica available. One pattern is to make the cloud database the read replica while the on-premise master continues to handle writes until the final cut-over. This lets you test query compatibility and index performance without impacting live workflows. At cut-over, you switch the master pointer to the new environment once synchronization confirms parity.
When you migrate to cloud data centers, design for latency and sovereignty. Decide whether to use your cloud master or to keep an on-premise version of your database for regulatory or latency reasons. For some setups, the database master in the cloud improves scalability and simplifies disaster recovery, but you must test the network links carefully. If you run instances of your application in the cloud, then ensure the application data to the cloud migrations include session state, cache warming, and connection pooling adjustments. Also plan for data writes to the on-premise system while synchronization continues, and define how to reconcile later.
Synchronise real-time updates via API bridges or message queues to prevent data drift and to maintain consistency across the new environment. Verify referential integrity, and run application acceptance tests that simulate normal and peak loads. After cut-over, verify application’s data access patterns, and monitor slow queries that could become a bottleneck. Keep production systems observable with dashboards that surface latency, error rates, and cache hit ratios. Use rollback plans that can restore the on-premise master and switch traffic back quickly if the cut-over exposes critical issues.
Work with your tos vendor and a migration expert who knows database while you troubleshoot and who can lead the final switchover. Document the phase of the migration, and capture lessons learned from the migration. This reduces future risk and increases confidence in your ability to complete the migration. If you consider hybrid deployments or edge compute, review cloud-versus-edge AI trade-offs to match latency and governance needs cloud versus edge AI.
Drowning in a full terminal with replans, exceptions and last-minute changes?
Discover what AI-driven planning can do for your terminal
data migration downtime
Assess risk and define acceptable outage windows aligned with vessel schedules. Business can tolerate some downtime during tightly scheduled maintenance windows, and you must confirm which windows are safe. Create a calendar that maps vessel ETA/ETD, peak gate periods, and planned maintenance so decision-makers choose cut-over times that minimize impact on the supply chain. For many terminals, migration is generally unacceptable during peak arrival windows, so plan for nighttime or low-traffic days when possible.
Build rollback and contingency plans to restore service quickly on failure. Document step-by-step rollback actions, and rehearse them in the sandbox environment. Prepare scripts and runbooks that automate common recovery tasks. Also provide operator checklists for validation after rollback. This reduces stress and shortens the amount of downtime if something goes wrong. Monitor performance metrics during cut-over to detect and resolve bottlenecks in real time. Use alerting thresholds for queue depth, transaction latency, and error rates so the team can react fast.
To minimize downtime, use synchronization strategies such as continuous replication, dual-write, and phased cut-over. Strategies to minimize downtime include keeping parallel systems live during validation and using message queues to buffer bursts. Quantify likely data migration downtime for each step, and plan mitigation actions for each risk. For example, if a large historical load could block switch-over, then consider pre-seeding the cloud or the new database with bulk data while the legacy system continues running.
Design KPIs to measure downtime impact: track the amount of downtime, container dwell time, gate wait time, and vessel turnaround variance. Include the migration team, operations leads, and IT in post-cut-over reviews. Verify that ensuring minimal downtime was achieved and update your migration playbooks with new insights. Remember that careful scheduling, robust rollback plans, and close monitoring are the core management strategies that can support a smooth transition and maintain business continuity throughout the migration.
best practices
Invest in comprehensive operator training and change-management programmes so staff adopt new workflows quickly. Training should include role-based simulations, checklists, and hands-on sessions in a sandbox environment. Use a mixture of classroom lessons and live practice runs. Include planners, dispatchers, and gate agents in regular drills so everyone knows how to react to exceptions. Change management should highlight benefits to daily work, and should offer clear escalation paths for issues that may arise.
Enforce cybersecurity controls: encryption, access governance and continuous monitoring. The IAPH guidelines note that loss of access to terminal operating systems during migration can have severe operational and security consequences, and they recommend tight access control and live monitoring (IAPH). Use zero-trust approaches where possible, and log every administrative action during cut-over for forensic traceability. Also validate compatibility between security appliances and the new OS to avoid unexpected blockages.
Track KPIs to measure migration success. Monitor turnaround time, throughput, and error rates so you can quantify gains or regressions. Ports that adopt advanced TOS solutions often see measurable productivity improvements when they follow best practices and phased roll-outs (regional report). Use continuous improvement loops and keep a lessons learned register. A migration offers the chance to update standards, refine automation, and improve data quality. For example, our RL-based agents at Loadmaster.ai can be trained in the terminal digital twin to reduce rehandles and to stabilise performance across shifts, which supports long-term operational resilience.
Finally, choose migration tools that fit your environment and governance needs. Whether you use replication, CDC, or message brokers, ensure the tools support auditability and rollback. Engage a migration expert for complex cut-overs, and document every migration phase in a detailed migration playbook. This comprehensive migration strategy will help you minimize downtime, protect data integrity, and complete the migration so the terminal benefits from a seamless upgrade with tangible performance improvements.
FAQ
What is the best migration approach for a busy container terminal?
Start with a clear migration plan that aligns objectives with KPIs and stakeholder needs. Use governance, pilot testing, and parallel running to protect business operations during cut-over.
How do migration strategies reduce disruption?
Phased roll-outs and parallel running let teams validate functionality without stopping operations. Pilots and incremental approaches reveal compatibility issues before full deployment.
What steps are included in the data migration process?
Inventory, mapping, extraction, transformation, and layered validation are key steps. Use automated checks plus manual spot audits to ensure data integrity and to prevent data loss.
How can I minimize downtime during database migration?
Use replication and log shipping so the new database stays synchronised while the old one runs. Also schedule cut-over windows around vessel timetables and test rollback routines thoroughly.
What is data migration downtime and how is it measured?
Data migration downtime is the period when services are limited due to migration activity. Measure it alongside operational KPIs such as container dwell time and gate wait time to understand business impact.
Which cybersecurity measures matter most during migration?
Implement strict access governance, encryption, and continuous monitoring. Follow industry guidance and keep audit trails of all administrative actions to support post-migration reviews.
How important is training for a successful migration?
Very important. Training reduces human errors and helps staff adapt to new workflows so the terminal experiences minimal disruption. Include scenario-based drills in the training plan.
When should we involve the tos vendor in the migration?
Engage the tos vendor early, ideally during planning and pilot phases. Their input helps with compatibility testing, data mapping, and final acceptance tests.
Can cloud migration help terminals scale operations?
Yes, cloud resources can offer elastic capacity for analytics and storage and can support disaster recovery. Assess latency, sovereignty, and cost concerns before choosing cloud data centers for critical services.
What are common lessons learned from migration projects?
Common lessons include the need for clear governance, the value of parallel running, and the importance of rehearsed rollback plans. Capture these lessons to improve future migrations and to ensure a smooth transition.
our products
 stowAI
stowAI
 stackAI
stackAI
 jobAI
jobAI
Innovates vessel planning. Faster rotation time of ships, increased flexibility towards shipping lines and customers.
Build the stack in the most efficient way. Increase moves per hour by reducing shifters and increase crane efficiency.
Get the most out of your equipment. Increase moves per hour by minimising waste and delays.
 stowAI
stowAI
Innovates vessel planning. Faster rotation time of ships, increased flexibility towards shipping lines and customers.
 stackAI
stackAI
Build the stack in the most efficient way. Increase moves per hour by reducing shifters and increase crane efficiency.
 jobAI
jobAI
Get the most out of your equipment. Increase moves per hour by minimising waste and delays.

