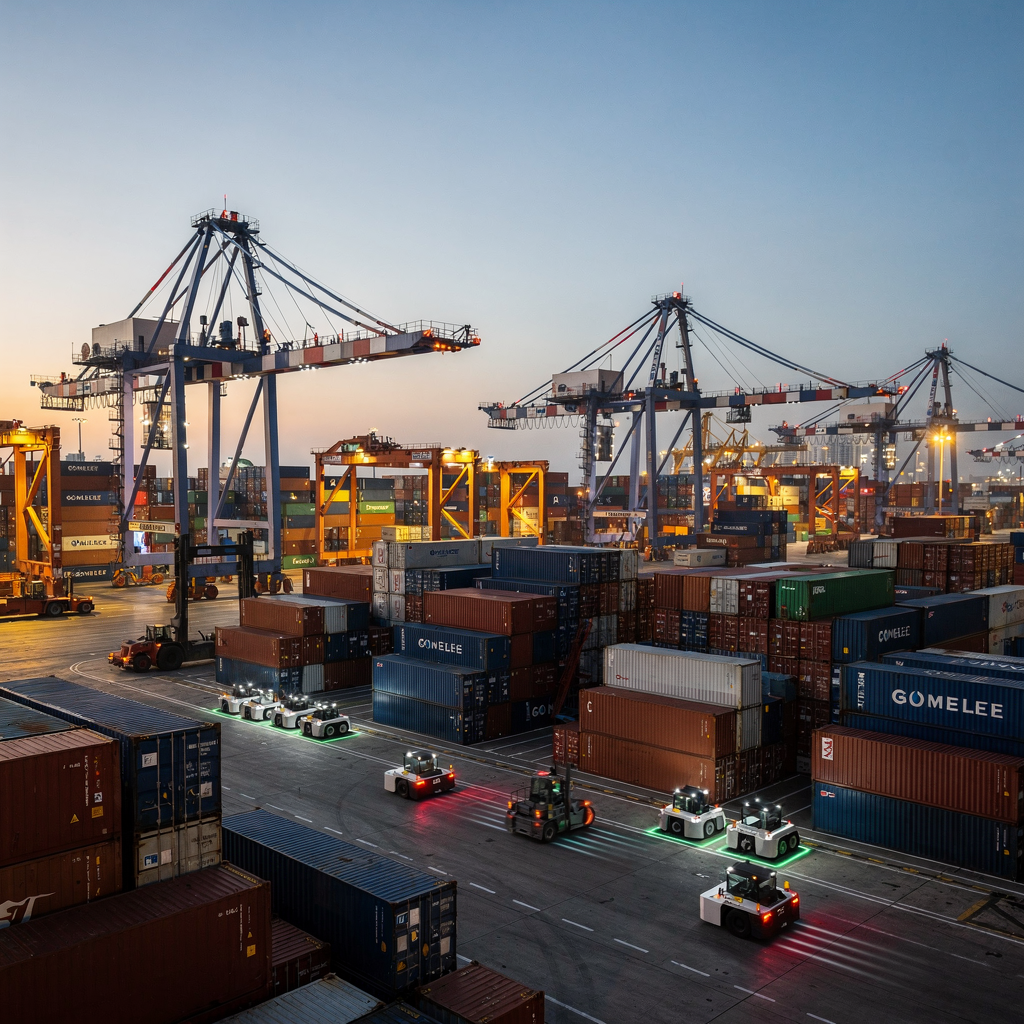
Understanding AI in Port and the Smart Port Ecosystem
Smart port concepts redefine how terminals run and how stakeholders coordinate. A smart port blends sensors, networks, DATA, and advanced control to improve throughput, lower emissions, and reduce costs. In practice, AI and artificial intelligence power new decision layers that reshape traditional port routines. The integration of AI across berths, yards, gates, and vessels enables a connected ecosystem where real-time telemetry and predictive analytics guide actions. For example, EU terminals that apply intelligent berth management report up to a 20% reduction in operational carbon emissions through improved scheduling and reduced idle time (PDF) AI-Enhanced Smart Maritime Logistics. This statistic highlights how data, models, and quick decisions allow ports to operate cleaner and faster.
Real-time data feeds such as vessel positions, berthing schedules, weather inputs, and equipment telemetry form the backbone of smarter decision making. These real-time streams feed AI analytics engines that evaluate trade-offs, predict conflicts, and propose sequences. For example, AI in port can forecast berth availability minutes or hours ahead, which reduces vessel waiting and fuel burn. The integration of AI with Terminal Operating Systems (TOS) and IoT sensors enables synchronized responses from quay cranes to yard trucks. Ports like the Port of Rotterdam and others in Europe pilot such flows to demonstrate measurable gains and to demonstrate how integrating ai and automation aids environmental targets.
Port management teams must adopt a systems view. They should combine governance, data quality, and human oversight to capture the full potential of AI. Loadmaster.ai works with terminals to spin up a digital twin and then train Reinforcement Learning agents so planners and dispatchers can move from firefighting to forward planning. In that way, ports navigate daily disruptions with policies that balance KPIs. This creates consistency so that outcomes do not hinge on one expert planner. The smart port idea thus becomes a practical path to efficiency and sustainability, while helping ports meet evolving sustainability goals with demonstrable metrics.
AI Tools and Logistics Operations
AI tools in modern terminals include predictive maintenance, computer vision, robotics, scheduling algorithms, and reinforcement learning agents. Predictive maintenance systems detect wear and forecast failures so teams can fix gear during low-impact windows. For instance, predictive maintenance reduces downtime and energy waste in handling equipment. Computer vision inspects containers and detects damages, while robotics and autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) move boxes with precision. Together these AI technologies provide a cohesive stack that improves throughput and reduces human exposure to repetitive tasks.
Logistics operations benefit in clear ways. Terminals that deploy AI-driven orchestration and yard strategies report cargo throughput improvements of 10–30%, which shortens dwell and lowers emissions from idling ships and trucks (PDF) AI-Enhanced Smart Maritime Logistics. IoT integration for container tracking and stock-yard planning gives dispatchers better situational awareness and faster recovery from disruptions. To explore how scheduling and job control handle cut-off events, terminals can review time-critical job scheduling for vessel cut-off management for concrete techniques time-critical job scheduling. This resource explains how policies and automation shorten reaction time and how AI tools coordinate quay, yard, and gate activity.
AI algorithms to predict container flows and to align resources help reduce empty moves and unnecessary reshuffles. Advanced computer vision combined with data fusion enables real-time inventory awareness, and Reinforcement Learning can then suggest actions that lower travel distance and even out workloads. For many terminals, adopting these ai technologies in port transforms tactical choices into strategic wins. Ports like Jeddah Islamic Port and the Port of Los Angeles have piloted automation and analytics programs that show both operational and environmental gains. As the power of AI grows, logistics teams gain more visibility and more consistent performance across shifts, which enables ports to handle larger vessel mixes while protecting service levels.

Drowning in a full terminal with replans, exceptions and last-minute changes?
Discover what AI-driven planning can do for your terminal
Optimise Operational Efficiency within Port
Optimising a terminal requires tight orchestration across quay, yard, and gate. AI-driven scheduling algorithms allocate berths, assign cranes, and sequence moves to minimize crane idle time and to balance yard density. These algorithms consider multiple KPIs and reweight goals as conditions change. For planners seeking deeper technical insight, exploring predictive berth availability modeling shows how forecasts can drive hour-by-hour allocations predictive berth availability modeling. Using such models, ports can optimize arrival windows and reduce tug and bunker consumption.
Energy-use dashboards matter as much as throughput dashboards. Smart dashboards ingest telemetry, tariff schedules, and equipment states so managers can reduce peak loads and shift consumption to lower-cost intervals. Smart ports using IoT and AI report energy savings near 18% through automated lighting, heating, and equipment management Smart, Green, and Sustainable. These savings occur when AI systems spot underused assets or when AI models forecast power spikes and enact mitigations. Pilots that automate charge scheduling for electric AGVs further reduce peak demand and improve battery life opportunity-charging strategies.
Machine-learning models for demand forecasting and resource allocation predict inbound volumes and advise early stacking plans. Rather than rely on historical averages, Reinforcement Learning agents simulate many scenarios in a digital twin, which yields robust policies that adapt to sudden changes. That approach reduces rehandles, shortens driving distances, and stabilises crane productivity. Loadmaster.ai’s StowAI, StackAI, and JobAI demonstrate closed-loop optimisation for quay planning, yard placement, and execution. As a result, ports operate with fewer surprises and higher consistency, which improves operational efficiency and reduces cost per move.
Automation, Port Traffic and Port Planning
Automation at the quay and in the yard changes how terminals schedule moves and manage safety. Autonomous cranes and automated stacking cranes speed handling and reduce accident risk. AGVs and Automated Rubber-Tyred Gantries (RTGs) remove variability in truck routing and in-yard travel. These systems enhance crane operations and reduce human exposure to hazardous tasks. Implementing ai and automation requires clear guardrails and robust testing; terminals often deploy automation in stages so staff can adapt and so control remains transparent.
AI-based port traffic management shortens vessel waiting times by coordinating pilot arrival, berth readiness, and gate flows. Systems that ingest vessel ETA feeds and berth-state telemetry can cut idle time and thus reduce fuel burn for waiting ships. Reports indicate that smart scheduling and traffic control have cut CO₂ emissions significantly in European ports as they optimise cargo handling and berth allocation Transitioning Towards Green Port Operations. Advanced simulation tools let planners test peak-period flows, to identify chokepoints, and to validate investments in additional equipment or yard layout changes.
Strategic port planning tools simulate decades of growth and short-term surges, which help authorities make data-backed capacity choices. These simulations enable ports to handle larger vessels and denser schedules without sacrificing service. They also allow port authorities and port operators to plan for shore-power uptake, for electrified equipment, and for renewable integration. Adding these capabilities helps ports operate greener while meeting the growth demands of global trade. As ports face congestion and shifting trade lanes, they must adopt data-driven planning and automation that reduce risks and improve resilience.
Drowning in a full terminal with replans, exceptions and last-minute changes?
Discover what AI-driven planning can do for your terminal
Digital Twin, AI Models and Sustainability
A digital twin of terminal assets provides a virtual environment for scenario testing, resilience analysis, and policy training. By running operations inside a digital twin, teams can train AI models without exposing live operations to risk. Loadmaster.ai spins up a digital twin to train Reinforcement Learning agents, which helps terminals achieve cold-start readiness and avoids teaching the AI past inefficiencies. The digital twin allows what-if experiments, such as simulating equipment failures or sudden surges, and it supports safer, faster adoption of new workflows.
AI models predict emissions, water pollutants, and energy consumption so managers can measure the impact of operational decisions. For instance, AI models estimate CO₂ output from idling ships and advise berth swaps or tug scheduling to lower the carbon footprint of port calls. Studies show ports implementing AI-driven smart logistics and digital twins can achieve a 15–25% reduction in CO₂ emissions and lower noise and water pollutant loads through better sequencing and resource allocation Transforming Ports for a Low-Carbon Future. These gains come from smarter stacking, fewer empty moves, and from energising shore-power and shore-side electrification.
AI systems can analyze data from wastewater treatment units, fuel consumption meters, and ambient sensors to tune operations for sustainability. When combined with policy levers such as low-emission windows and differentiated port tariffs, the digital twin and AI models help operators meet regulatory and corporate sustainability goals. The transition to AI must include cybersecurity, data governance, and stakeholder training. When adopted carefully, advanced AI and digital twin methods both improve resilience and support long-term environmental targets.
Smarter Operations for a Greener Port
Combined, AI, automation, and digital twins power continuous operational improvement. They allow ports to automate repetitive tasks, to optimize sequences, and to surface insights that planners use to balance quay and yard trade-offs. Smarter operations reduce fuel use, lower maintenance costs, and shorten cargo dwell. They also help ports meet corporate commitments for emissions reduction and for community impacts. As AI continues to evolve, terminals will gain richer models that make day-to-day operations more predictable and less energy-intensive.
Stakeholder collaboration is key. Port authorities, shipping lines, terminal operators, equipment OEMs, and regulators should define shared KPIs and data interfaces. Practical projects include coordinated ETA sharing, shore-power incentives, and joint trials of electric handling equipment. For more concrete ways to identify underused capacity and to prove ROI, teams can consult resources on identifying hidden capacity and measuring ROI of AI pilots identifying hidden capacity and measuring ROI of AI. Such materials help ports make the case for investment and to prioritise pilots that deliver both service and sustainability gains.
Looking ahead, the future of global trade will be shaped by smarter, greener terminals that embrace AI and renewables. Ports must integrate renewable energy, scale shore-power, and adopt multi-objective AI that balances CO₂, cost, and throughput. By implementing robust digital twins and by adopting AI solutions that learn via simulation rather than only from history, ports can achieve significant improvements in efficiency while protecting community and environmental values. The culture of innovation will determine how quickly busy hubs such as the busiest ports can transition to low-carbon operations, reshaping how ports enable the maritime industry and secure a cleaner supply chain.
FAQ
What is a smart port?
A smart port uses sensors, networks, and AI to coordinate berth, quay, yard, and gate activity for better throughput and lower emissions. It combines real-time data and automation to improve decisions and to support sustainable practices.
How does AI reduce emissions in ports?
AI reduces emissions by optimizing vessel scheduling, minimizing idle time, and improving equipment use. For example, intelligent berth management has cut operational carbon in pilots by as much as 20% (PDF) AI-Enhanced Smart Maritime Logistics.
Can digital twins help with port planning?
Yes. Digital twin simulations let planners test peak flows, equipment failures, and electrification scenarios without risking live operations. They also enable reinforcement learning agents to train policies that generalise to live terminals.
What are common AI tools used in terminals?
Common tools include predictive maintenance models, computer vision for inspections, scheduling algorithms, AGV coordination, and reinforcement learning for multi-objective control. These tools improve throughput and reduce rehandles.
How do ports ensure safety when automating?
Terminals combine staged rollouts, operational guardrails, and rigorous sandbox testing in a digital twin before go-live. They also keep human oversight and audit trails to meet governance and regulatory needs.
What role do port authorities play in sustainability?
Port authorities set policy, invest in shore-power and charging infrastructure, and coordinate multi-stakeholder efforts to reduce emissions. They also define KPIs and incentives that encourage greener operations.
How fast can a terminal implement AI?
Implementation speed depends on scope: pilots for scheduling or predictive maintenance can launch in months, while full automation projects may take years. Using simulation-first approaches can deliver value quickly without long historical data requirements.
Is historical data required to deploy AI in ports?
Not always. Approaches that use digital twins and reinforcement learning can train policies without large historical datasets, which helps terminals that lack clean history to still benefit from AI.
What savings can ports expect from AI and automation?
Savings vary, but studies show energy reductions near 18% and emission reductions between 15–25% for smart ports using AI and IoT interventions Smart, Green, and Sustainable and Transforming Ports for a Low-Carbon Future. Operational throughput can improve by 10–30% in some cases.
How can terminals measure ROI from AI?
Terminals should track KPIs such as moves per hour, average truck turnaround, fuel consumption, and CO₂ per TEU, then compare pilot outcomes to baseline performance. Resources on measuring ROI and on identifying hidden capacity can guide metric selection and pilot design measuring ROI of AI.
our products
 stowAI
stowAI
 stackAI
stackAI
 jobAI
jobAI
Innovates vessel planning. Faster rotation time of ships, increased flexibility towards shipping lines and customers.
Build the stack in the most efficient way. Increase moves per hour by reducing shifters and increase crane efficiency.
Get the most out of your equipment. Increase moves per hour by minimising waste and delays.
 stowAI
stowAI
Innovates vessel planning. Faster rotation time of ships, increased flexibility towards shipping lines and customers.
 stackAI
stackAI
Build the stack in the most efficient way. Increase moves per hour by reducing shifters and increase crane efficiency.
 jobAI
jobAI
Get the most out of your equipment. Increase moves per hour by minimising waste and delays.

